Laparoscopic Hemorrhoidectomy
Stapled hemorrhoidectomy, also known as stapled hemorrhoidopexy or procedure for prolapse and hemorrhoids (PPH), is a surgical technique used to treat hemorrhoids, which are swollen and inflamed veins in the rectum and anus. This procedure is primarily designed to address internal hemorrhoids and is often considered a minimally invasive alternative to traditional hemorrhoidectomy.
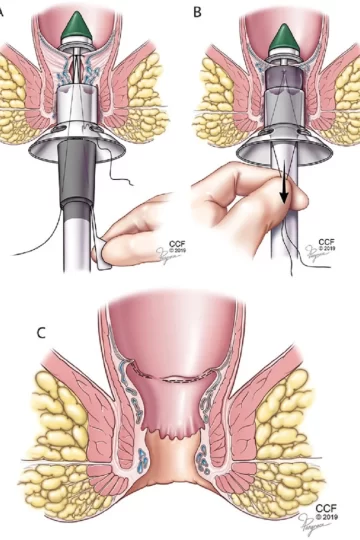
The procedure involves using a circular stapling device to remove excess tissue and reposition the hemorrhoidal cushions back to their normal anatomical position within the anal canal. The goal of stapled hemorrhoidectomy is to reduce the prolapse of hemorrhoidal tissue while minimizing postoperative pain and promoting faster recovery compared to conventional surgical methods.
Here is an overview of the key aspects of stapled hemorrhoidectomy:
Indications:
Stapled hemorrhoidectomy is typically indicated for patients with symptomatic internal hemorrhoids that have not responded to conservative treatments such as fiber supplements, topical medications, and lifestyle modifications. Common symptoms of internal hemorrhoids include bleeding, prolapse, discomfort, itching, and pain during bowel movements.
Procedure:
During a stapled hemorrhoidectomy, the patient is placed under general or regional anesthesia. The surgeon inserts a specialized stapling device through the anal canal to remove a ring of excess internal hemorrhoidal tissue and reposition the remaining tissue higher in the anal canal. This effectively interrupts the blood flow to the excessive internal hemorrhoidal tissue, promoting shrinkage and reducing symptoms.
Recovery:
After the procedure, patients may experience minor discomfort, and there may be some bleeding during bowel movements. However, the recovery period is generally shorter compared to traditional hemorrhoidectomy, with many patients able to return to normal activities sooner.
Postoperative care:
Postoperative care following stapled hemorrhoidectomy may include dietary modifications, such as increasing fiber intake, staying hydrated, and taking stool softeners to promote regular and comfortable bowel movements. Patients are typically advised to avoid straining during bowel movements and to follow specific instructions provided by their healthcare provider.
Benefits:
The key benefits of stapled hemorrhoidectomy include reduced postoperative pain, faster recovery, and potentially shorter hospital stays when compared to conventional hemorrhoidectomy. Patients may also experience less discomfort during the immediate postoperative period, which can contribute to an improved overall surgical experience.
Alternatives:
In addition to stapled hemorrhoidectomy, alternative treatment options for hemorrhoids include traditional hemorrhoidectomy (surgical removal of hemorrhoidal tissue), rubber band ligation, sclerotherapy, and infrared coagulation. The choice of treatment depends on factors such as the severity of hemorrhoidal symptoms, patient preferences, and the recommendations of a healthcare provider.
Follow-up:
Postoperative follow-up with a healthcare provider is important to monitor the healing process, address any potential complications, and ensure that the patient’s symptoms are effectively managed. Follow-up appointments may involve physical examinations and discussions about ongoing symptom management and lifestyle modifications.
In conclusion, stapled hemorrhoidectomy is a surgical technique designed to address symptomatic internal hemorrhoids while minimizing postoperative pain and promoting faster recovery. It is essential for individuals considering this procedure to have a comprehensive discussion with their healthcare provider to understand the potential benefits, risks, and expected outcomes based on their specific health needs and circumstances.