Peripheral Angiography
Peripheral Angiography
Peripheral angiography is a diagnostic procedure that involves the use of X-ray and contrast dye to visualize the blood vessels in the peripheral (outside the heart and brain) regions of the body. The procedure is commonly performed to assess the presence of arterial blockages, narrowing, or other abnormalities. However, it is important to note that when talking about PDA (Patent Ductus Arteriosus), the anomaly is usually associated with the heart rather than the peripheral arteries. PDA is a congenital heart defect where a connection (ductus arteriosus) between two major blood vessels, the aorta and the pulmonary artery, fails to close after birth.
If you are referring to the peripheral angiography in the context of PDA, it might be a misinterpretation, and you may be actually looking for cardiac catheterization or angiography for evaluating the PDA in the heart.
Here’s an overview of how cardiac catheterization may be used to assess PDA:
- Cardiac Catheterization for PDA:
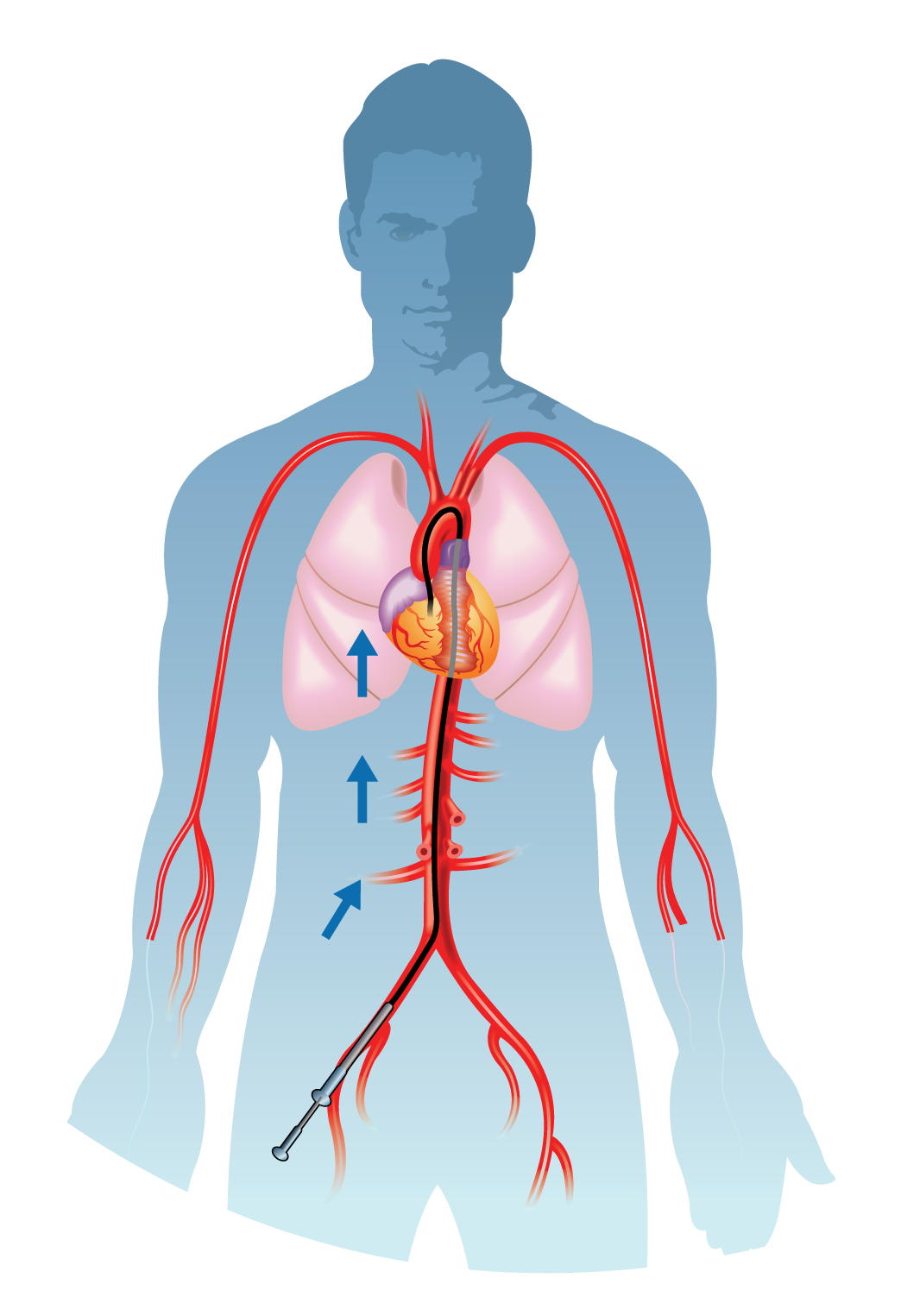
- Cardiac catheterization involves the insertion of a catheter into the blood vessels to gain access to the heart. In the case of PDA, the catheter is usually threaded through the blood vessels from the groin to the heart.
- A contrast dye is injected through the catheter into the heart chambers and vessels, making them visible on X-ray images.
- The imaging allows the cardiologist to assess the size, location, and characteristics of the PDA.
2. Closure of PDA:
-
- Depending on the findings, the procedure may involve closing the PDA using various techniques. One common method is the placement of a closure device through the catheter.
3. Benefits:
-
- Cardiac catheterization for PDA helps the healthcare team determine the best course of action, whether it involves monitoring the PDA, administering medical treatment, or performing a catheter-based closure procedure.
4. Risks and Complications:
-
- As with any medical procedure, cardiac catheterization carries some risks, including bleeding, infection, and injury to blood vessels. The risks are generally low, and the benefits of accurate diagnosis and potential intervention often outweigh them.
5. Follow-Up:
-
- Patients typically undergo follow-up assessments to ensure the effectiveness of the intervention and to monitor for any complications.
If you are specifically looking for peripheral angiography for a different condition or reason, please provide additional details, and I’ll be happy to offer more information.
Approach
For everyday care or life-changing care you can count on our doctors.
Experts
You can count on us to keep you and your loved ones safe and healthy.
Technology
Cardiac rehabilitation (CR) can slow or reverse the nurse progression.
Facilities
We use a team approach to providing health care, and involve the patient.
Peripheral Angiography
It seems like you may be referring to a scenario where there are restrictions or limitations related to coronary angioplasty. If you have specific details or concerns in mind, please provide more information so I can offer a more accurate response.
Coronary angioplasty, or percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), involves dilating narrowed coronary arteries. A catheter with a deflated balloon is advanced to the blockage site. Upon reaching the narrowed segment, the balloon is inflated, compressing the plaque and widening the artery. This dilation restores blood flow, relieving symptoms and improving overall cardiac function.
Coronary angioplasty is a procedure primarily used to address coronary artery blockages. However, for hypertrophic conditions like hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), angioplasty may not be the first-line treatment. HCM involves thickening of the heart muscle and is typically managed through medications, lifestyle changes, or in severe cases, surgery. Angioplasty isn’t a standard approach for hypertrophic conditions. Always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
Coronary angioplasty primarily addresses blockages in coronary arteries supplying blood to the heart muscle. It isn’t typically performed in the right ventricle, which is a chamber of the heart responsible for pumping blood to the lungs. Procedures involving the right ventricle, such as right heart catheterization, differ and are usually conducted for specific diagnostic purposes or conditions affecting that particular heart chamber. Always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized medical advice.
Related TreatmentPeripheral Angiography
Peripheral Angiography is primarily a diagnostic procedure used to visualize blood vessels, and its direct application to treatment is limited. However, the information obtained from this procedure can guide further treatment decisions.
