AICD
AICD
A specialized implantation device called an intracardiac defibrillator (ICD) or automatic implantable cardioverter defibrillator (AICD) is used to monitor and control the heart’s rhythm. Patients at risk of potentially fatal ventricular arrhythmias, such as ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation, are the main population for which it is prescribed.
Key features of an ICD include:
- Defibrillation Functionality:
- The primary function of an ICD is to deliver an electrical shock to the heart to terminate dangerous arrhythmias. If the device detects a rapid and irregular heartbeat that could lead to ventricular fibrillation, it automatically delivers a high-energy shock to restore the heart’s normal rhythm.
- Pacing Functionality:
- In addition to defibrillation capabilities, many ICDs also have pacing functions similar to those found in traditional pacemakers. They can provide pacing therapy to regulate the heart rate and rhythm in case of bradycardia (slow heart rate).
- Monitoring and Detection:
- The ICD continuously monitors the heart’s activity. Sophisticated algorithms analyze the heart’s electrical signals to detect abnormal rhythms. If a dangerous arrhythmia is identified, the device responds accordingly.
4. Implantation:
- The ICD is typically implanted under the skin, usually in the chest area, with leads (thin insulated wires) threaded through veins into the heart. These leads are connected to the device and allow for the sensing and delivery of electrical impulses.
5. Battery and Longevity:
-
- ICDs are powered by batteries that have a finite lifespan. The lifespan depends on factors such as device programming, usage, and battery capacity. When the battery is depleted, the entire device needs to be replaced through a surgical procedure.
ICDs are commonly prescribed for individuals who have experienced or are at risk of ventricular arrhythmias, especially those who have survived sudden cardiac arrest or have certain heart conditions that increase their risk. Additionally, some ICDs may have additional features, such as monitoring fluid levels in the lungs to provide information about heart failure status.
As with any medical device, the decision to implant an ICD is made based on the patient’s specific clinical situation, and the implantation is typically performed by a cardiologist or electrophysiologist, who are specialists in the management of heart rhythm disorders.
Approach
For everyday care or life-changing care you can count on our doctors.
Experts
You can count on us to keep you and your loved ones safe and healthy.
Technology
Cardiac rehabilitation (CR) can slow or reverse the nurse progression.
Facilities
We use a team approach to providing health care, and involve the patient.
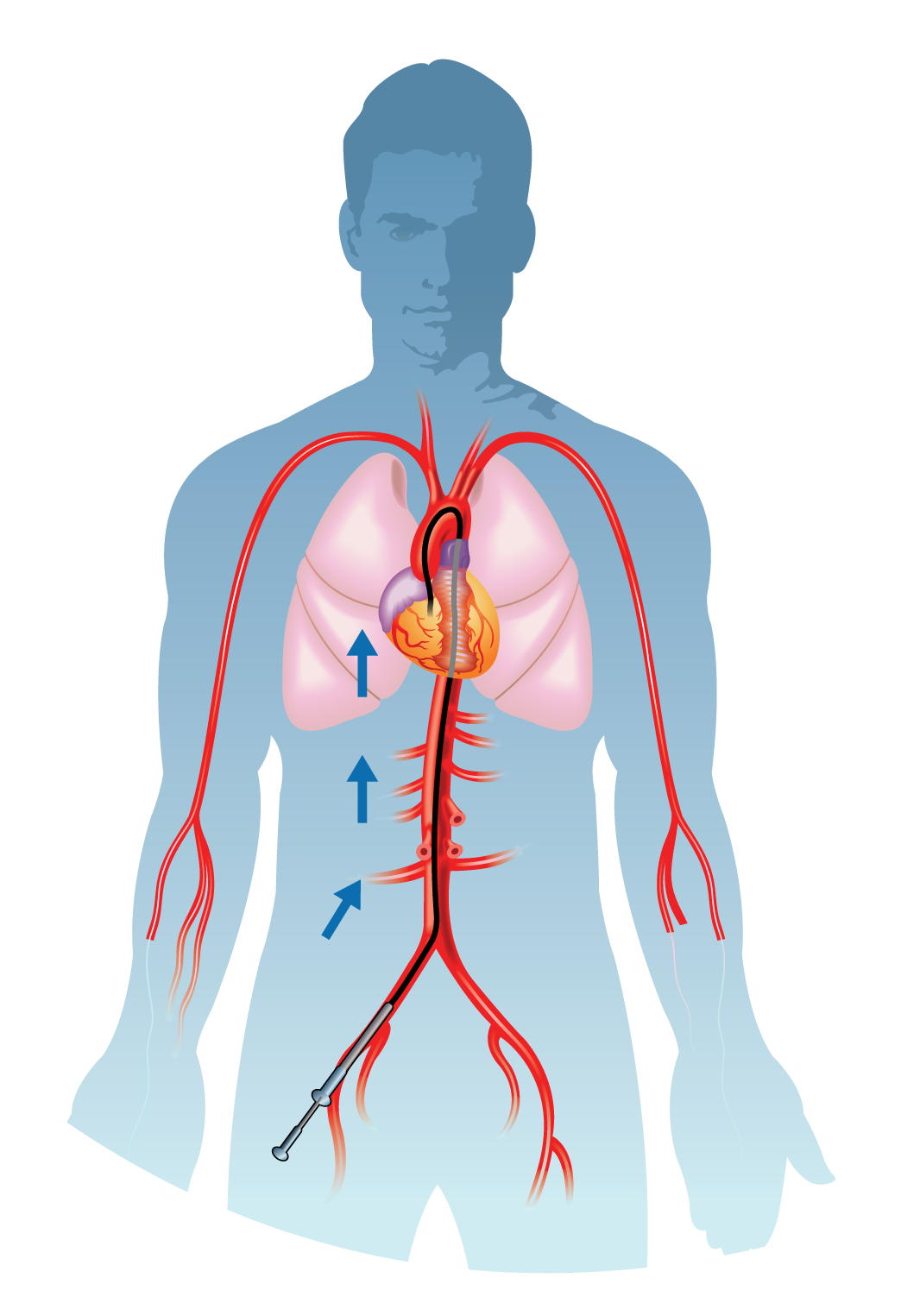
Automatic Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (AICD)
It seems like you may be referring to a scenario where there are restrictions or limitations related to coronary angioplasty. If you have specific details or concerns in mind, please provide more information so I can offer a more accurate response.
Coronary angioplasty, or percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), involves dilating narrowed coronary arteries. A catheter with a deflated balloon is advanced to the blockage site. Upon reaching the narrowed segment, the balloon is inflated, compressing the plaque and widening the artery. This dilation restores blood flow, relieving symptoms and improving overall cardiac function.
Coronary angioplasty is a procedure primarily used to address coronary artery blockages. However, for hypertrophic conditions like hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), angioplasty may not be the first-line treatment. HCM involves thickening of the heart muscle and is typically managed through medications, lifestyle changes, or in severe cases, surgery. Angioplasty isn’t a standard approach for hypertrophic conditions. Always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
Coronary angioplasty primarily addresses blockages in coronary arteries supplying blood to the heart muscle. It isn’t typically performed in the right ventricle, which is a chamber of the heart responsible for pumping blood to the lungs. Procedures involving the right ventricle, such as right heart catheterization, differ and are usually conducted for specific diagnostic purposes or conditions affecting that particular heart chamber. Always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized medical advice.
Related TreatmentAICD
Angioplasty uses a tiny balloon catheter that is inserted in a blocked blood vessel to help widen it and improve blood flow to your heart. Angioplasty is often combined with the placement of a small wire mesh tube called a stent. The stent helps prop the artery open, decreasing its chance of narrowing again.
